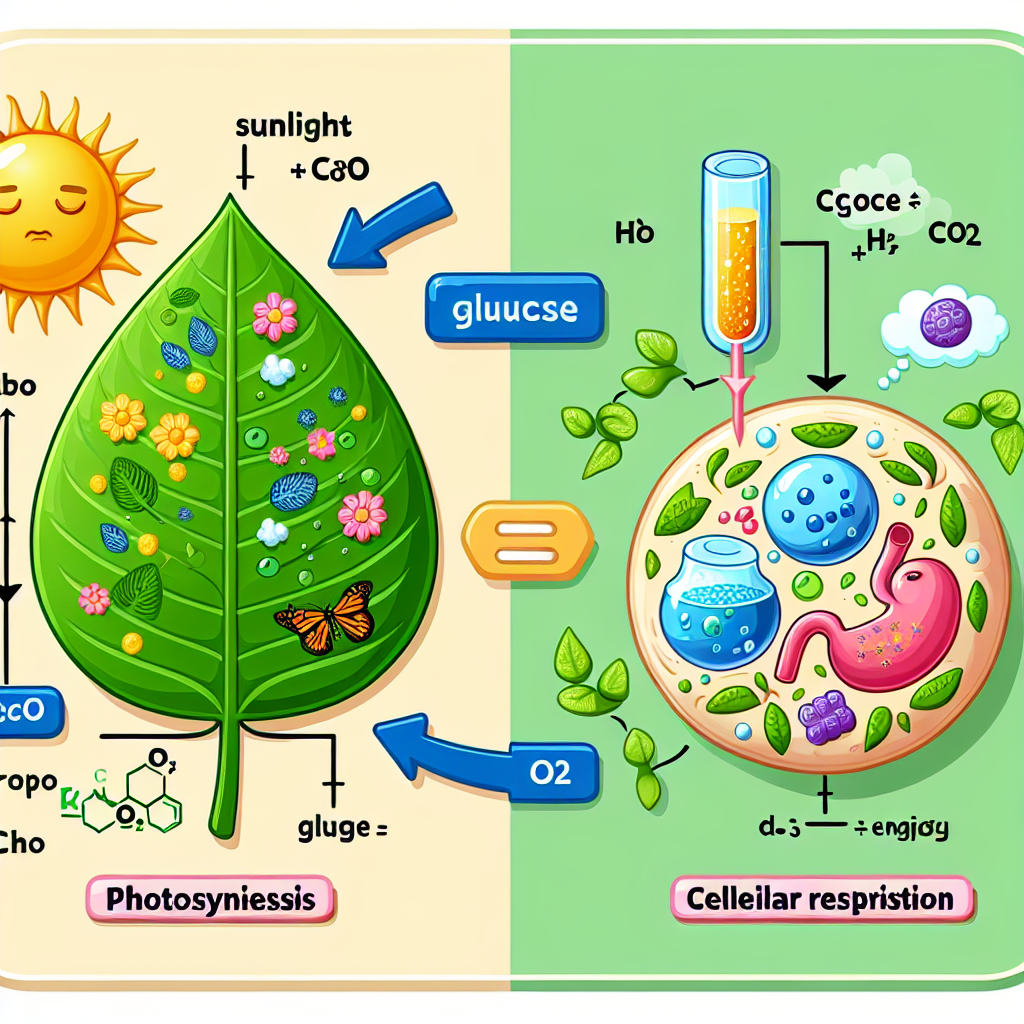
As we delve into the fascinating world of biology, it’s inevitable that we explore the fundamental processes of life itself, primarily photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Both of these biological processes are integral to the survival of life on Earth, yet they operate differently. A question often posed is: what is the difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? In this article, we will explore these processes separately, and then contrast the two to highlight their differences.
Understanding the Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy in the form of glucose, or sugar. This process takes place in a plant cell’s chloroplasts, which contain pigments (such as chlorophyll) that absorb light. The process of photosynthesis can be divided into two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin Cycle).
During the light-dependent reactions, the absorbed light energy is used to create two high-energy compounds: ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These compounds then power the second stage of photosynthesis, the Calvin Cycle, where carbon dioxide is converted into glucose. This glucose is then used by the plant for growth and development, while also acting as a primary food source for many organisms. Thus, photosynthesis not only provides energy for the plants themselves but also indirectly sustains many other forms of life.
The unique aspect of photosynthesis is that it essentially converts the sun’s light energy into chemical energy, which can be stored and used when needed. It’s also responsible for producing oxygen as a byproduct, which is released into the atmosphere and is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms, including humans.
The Mechanism behind Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration, on the other hand, is a process that occurs in all aerobic organisms, including plants and animals. It involves the breakdown of glucose molecules to produce ATP, the energy currency of cells. Unlike photosynthesis, cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of the cell and can be divided into three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into a molecule called pyruvate. This process occurs in the cytoplasm and generates a small amount of ATP. Next, in the Krebs cycle, the pyruvate is further broken down and releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct. The final stage, oxidative phosphorylation, uses the molecules produced in the previous steps to generate a large amount of ATP.
Cellular respiration essentially reverses the process of photosynthesis. It takes the glucose produced during photosynthesis and breaks it down to release energy in the form of ATP. It also produces carbon dioxide and water as byproducts, which are then released into the environment.
In answering the question "what is the difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration", we find that the two processes are distinct yet interconnected. While photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy and produces oxygen, cellular respiration takes this stored chemical energy and breaks it down to produce ATP, releasing carbon dioxide in the process. They are two halves of a cycle that sustains life on Earth, with photosynthesis providing the energy and oxygen needed for cellular respiration, and cellular respiration producing the carbon dioxide required for photosynthesis. Understanding these fundamental biological processes not only answers the question of what is the difference, but it also gives us a greater appreciation of the complex interplay that drives life on our planet.